AirTags vs. GPS vs. Bluetooth Trackers: Choosing the Best Asset Tracking Solution
Keeping track of valuable business assets—whether it's equipment, vehicles, tools, or inventory—is critical for operational efficiency and security. With multiple tracking technologies available, choosing the right solution can significantly impact your business's bottom line.
In this guide, we'll compare Apple AirTags, GPS trackers, and Bluetooth trackers, highlighting their strengths and limitations, and help you determine the best tracking solution for your business needs.
![]()
Quick Comparison: AirTags, GPS, and Bluetooth Trackers
| Feature | AirTags | GPS Trackers | Bluetooth Trackers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | ✅ Low ($6-26) | ❌ High ($50-$300) | ✅ Low ($15-$40) |
| Monthly Fees | ✅ None | ❌ $5-$40/month | ✅ None (mostly) |
| Battery Life | ✅ 1-5 years | ❌ Days-weeks | ✅ 6-12 months |
| Range | ✅ Global (via Apple devices) | ✅ Global (via satellites) | ❌ Limited (~30m) |
| Coverage (Urban) | ✅ Excellent | ✅ Good | ❌ Limited |
| Coverage (Rural) | ⚠️ Moderate | ✅ Excellent | ❌ Limited |
| Real-time Updates | ⚠️ Periodic | ⚠️ Varies | ❌ Only in range |
| Indoor Effectiveness | ✅ Good | ❌ Poor | ⚠️ Good, Limited |
| Enterprise Integration | ✅ Excellent (AirPinpoint API) | ⚠️ Moderate | Good |
Understanding Tracking Technologies for Business
Apple AirTags: The Crowd-Sourced Approach
How AirTags Work: AirTags use Apple's Find My network—a system that leverages the hundreds of millions of Apple devices worldwide. When your AirTag is lost, it sends out a secure Bluetooth signal that nearby Apple devices detect and relay to you, all anonymously and encrypted.
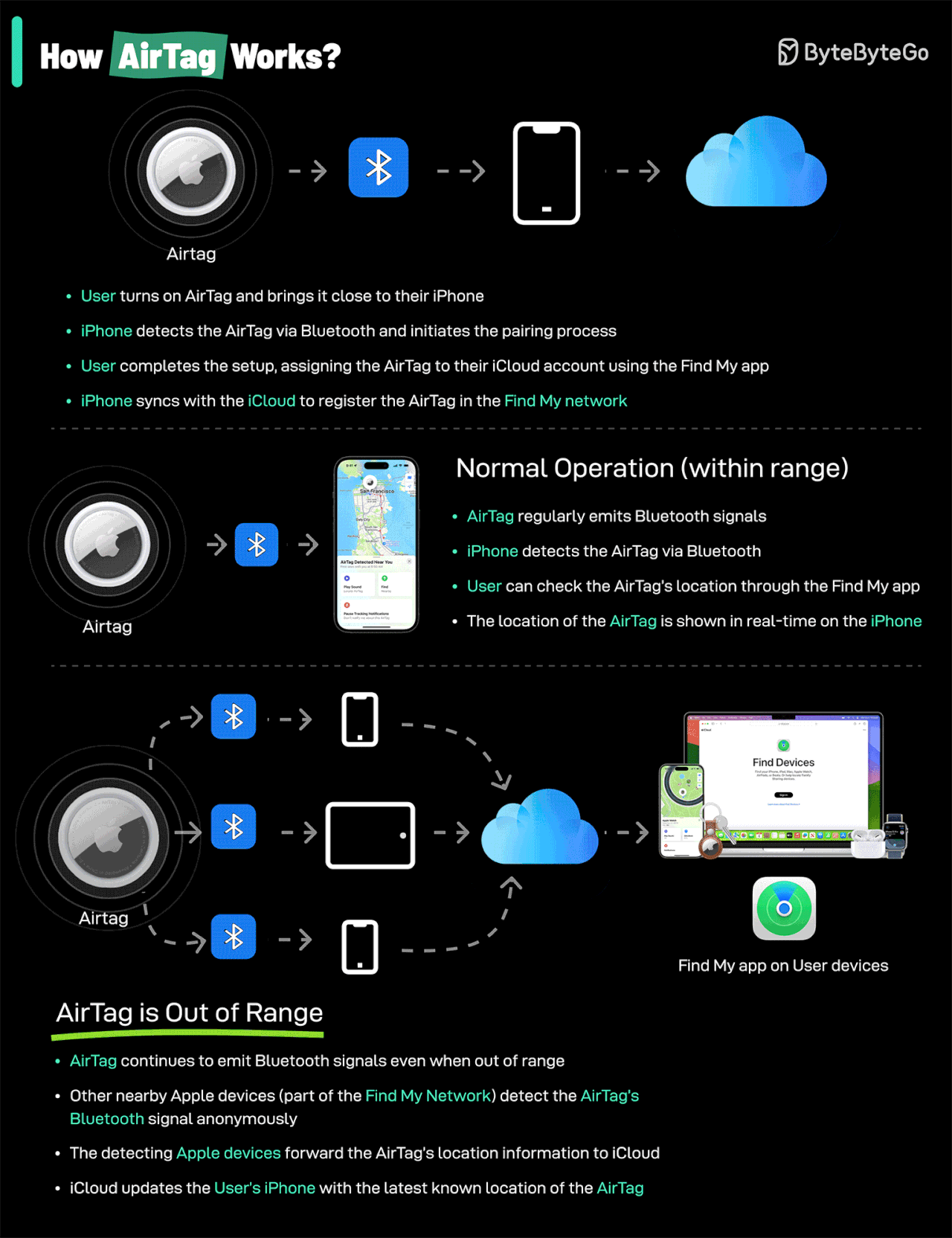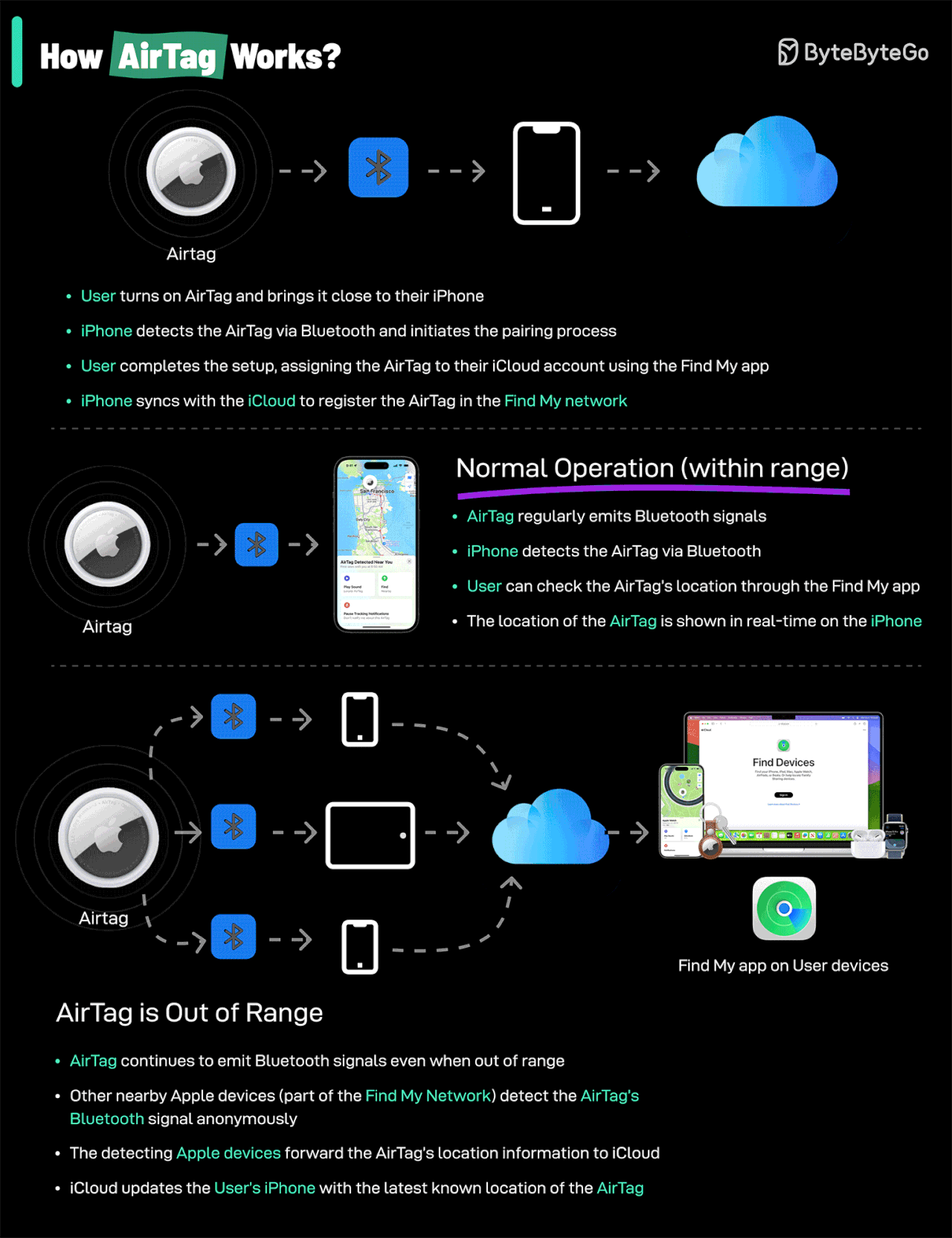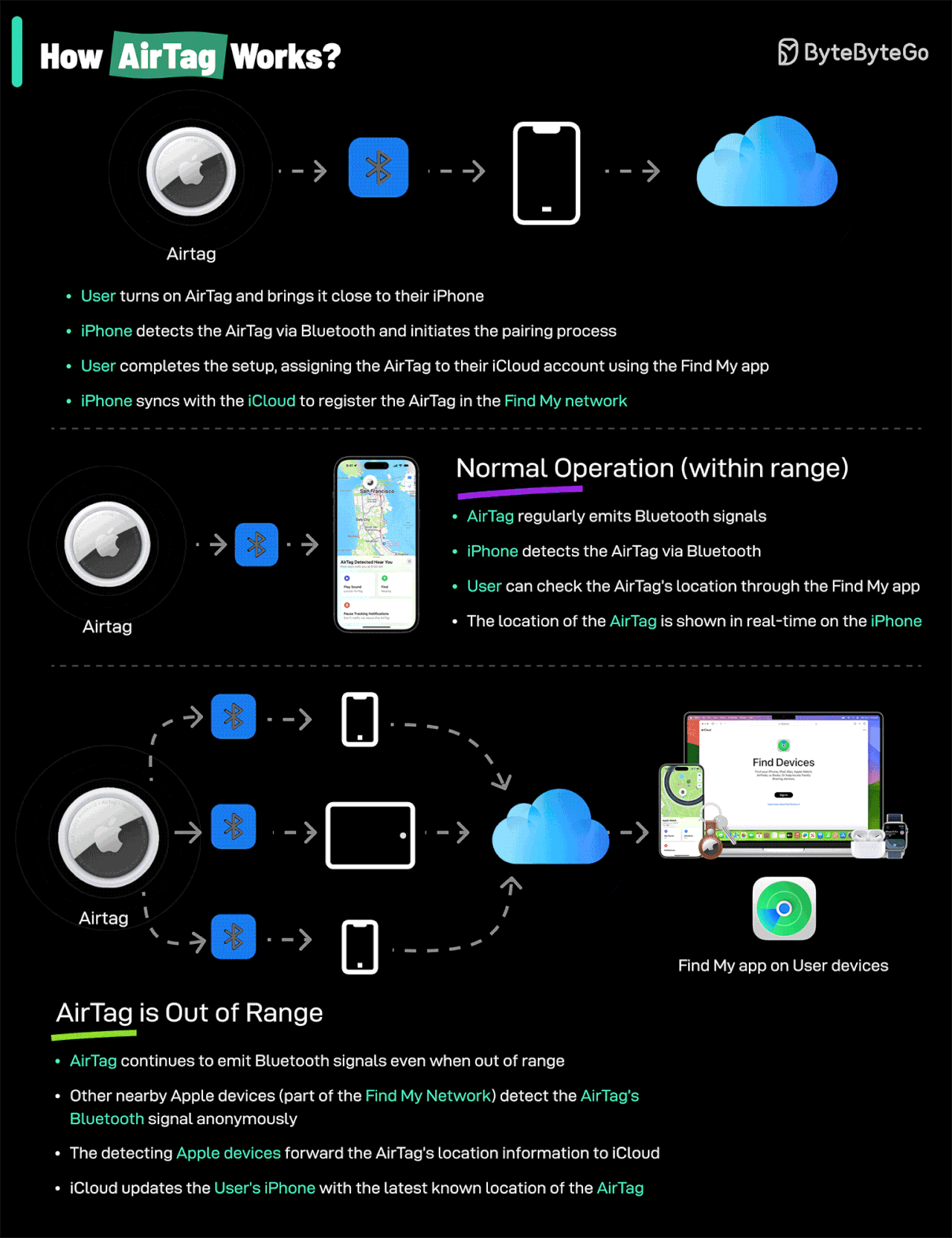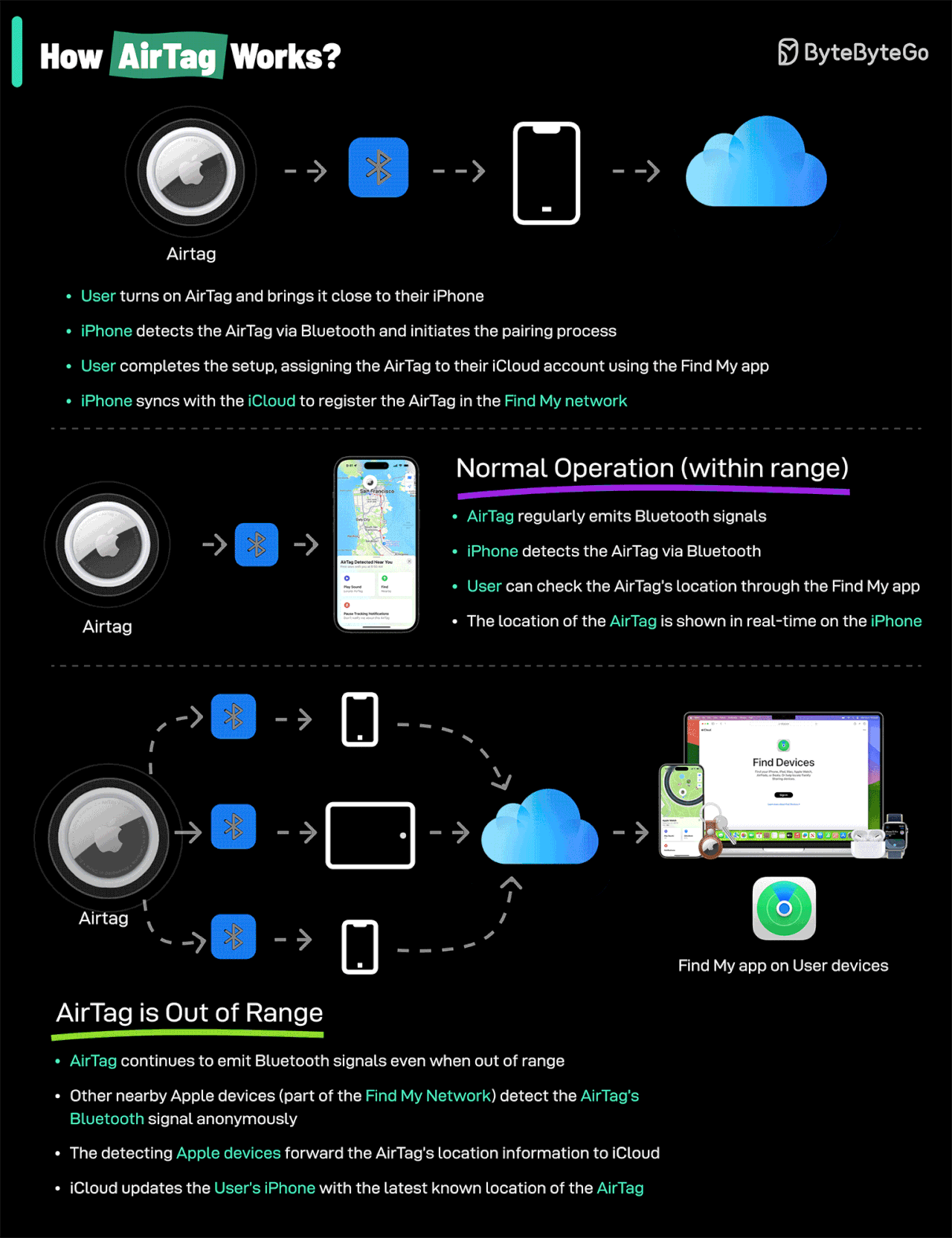 Credit: ByteByteGo
Credit: ByteByteGo
Apple AirTags: Leveraging the Power of Apple's Global Network
AirTags utilize Apple's extensive Find My network, harnessing hundreds of millions of Apple devices worldwide. When an AirTag-equipped asset is misplaced, nearby Apple devices anonymously relay its location securely back to you.
Business Advantages:
- Long Battery Life: 1-7+ years depending on model (standard AirTags: 1 year, AirPinpoint Tags: 3-5 years).
- Compact and Discreet: Easily attachable to tools, equipment, and inventory.
- Global Coverage: Effective wherever Apple devices are present, ideal for urban and suburban business environments.
- Cost-Effective: Low monthly fees, minimal maintenance, and affordable initial investment.
- Enterprise Integration: AirPinpoint API provides seamless integration with inventory management and asset tracking systems.
Limitations:
- Dependent on Apple device density; less effective in remote rural areas.
- Limited Android compatibility.
Ideal For: Asset tracking, inventory management, equipment monitoring, fleet management, and enterprise environments with moderate to high Apple device presence.
GPS Trackers: Satellite-Based Precision
GPS trackers communicate directly with satellites, providing precise location data transmitted via cellular networks. This technology is robust but comes with higher costs and maintenance requirements.
Business Advantages:
- Global Coverage: Reliable tracking in remote locations with clear sky visibility.
- Precise Location Data: Typically accurate within 10-50 feet outdoors.
- Advanced Features: Geofencing, speed monitoring, and detailed location history.
Limitations:
- High monthly subscription fees ($5-$40/month per device).
- Short battery life (days to weeks), requiring frequent maintenance.
- Poor indoor performance and bulky form factor.
Ideal For: Vehicles with constant power sources, heavy machinery, remote equipment tracking, and high-value assets in rural or remote locations.
Bluetooth Trackers: Short-Range, Low-Cost Solutions
Bluetooth trackers communicate directly with your smartphone or dedicated gateways, providing proximity-based tracking within a limited range.
Business Advantages:
- Low initial cost and low monthly fees.
- Suitable for small-scale indoor tracking (e.g., office equipment).
Limitations:
- Extremely limited range (~30 meters).
- No true location data or remote tracking capability.
- Ineffective for large-scale or outdoor asset tracking.
Ideal For: Small indoor environments, stationary office assets, and low-value items.
Why Businesses Prefer AirTags and AirPinpoint Tags
AirTags and AirPinpoint Tags offer a unique combination of affordability, reliability, and extensive coverage, making them ideal for most business tracking needs.
AirPinpoint Enterprise: Built for Business
AirPinpoint Tags enhance standard AirTags with enterprise-grade features:
- Extended Battery Life: 3-5 years without maintenance.
- Global Coverage: Leverages multiple networks for redundancy.
- Advanced Security: End-to-end encryption and robust access controls.
- Detailed Analytics: Motion tracking, temperature monitoring, and usage insights.
- Scalable Management: Centralized dashboard for managing thousands of assets effortlessly.
Real-World Business Use Cases
Scenario 1: Fleet and Vehicle Management
Recommended: AirTags or AirPinpoint Tags
- Cost-effective compared to traditional GPS trackers.
- Easy to conceal within vehicles, reducing theft risk.
- Reliable urban and suburban coverage.
Scenario 2: Vehicle Tracking
Best Choice: OBD2 GPS Tracker or AirTags
- Consistent power from the vehicle solves battery limitations
- Reliable coverage everywhere, including remote areas
- More detailed data like speed and route history
- OBD2 Trackers can meet ELD requirements, and report fuel, speed, engine idle time, etc.
- OBD2 Trackers can be easily found by thiefs, AirTags can be hidden
Scenario 3: High-Value Equipment and Tools
Best Choice: AirPinpoint Tags
- Extended battery life reduces maintenance overhead.
- Compact and discreet, ideal for expensive tools and equipment.
- Seamless integration with asset management systems via AirPinpoint API.
Scenario 4: Inventory and Supply Chain Management
Recommended: AirPinpoint Enterprise
- Real-time location updates across multiple facilities.
- Integration with existing inventory management systems.
- Advanced analytics for asset utilization and movement patterns.
- Automatic asset tracking eliminates manual check-in/out systems that floor workers typically avoid using.
Battery Life: The Real-World Perspective
Battery life is often misunderstood. Here's the reality:
- AirTags: Consistent 1-year battery life, easily replaceable ($1-2 per battery).
- AirPinpoint Tags: 3-5 years battery life, ideal for low-maintenance business operations.
- GPS Trackers: Frequent charging required (days to weeks), increasing operational overhead. Long term battery life can be achieved by doing low (1-2) updates per day
- Bluetooth Trackers: Typically 6-18 months, limited by proximity requirements.
Choosing the Right Tracker: Key Questions for Businesses
When selecting a tracking solution, consider:
- What assets am I tracking? (AirTags and AirPinpoint excel for equipment, tools, and vehicles, while GPS trackers may be better for assets in remote areas. OBD2 GPS Trackers are best for full data vehicle tracking.)
- Where will tracking occur? (AirTags are ideal for urban/suburban environments with Apple device density; GPS for remote rural locations with clear sky visibility.)
- How frequently do I need updates? (AirTags provide an optimal balance of timeliness and battery efficiency; GPS trackers offer more frequent updates at higher cost and power consumption.)
- What is my budget? (AirTags and AirPinpoint offer significantly lower total cost of ownership and maintenance, though GPS may justify its cost for specific high-security applications.)
- What's your maintenance tolerance? (Consider how frequently you're willing to replace batteries or charge devices across your asset fleet.)
Conclusion: Why AirTags and AirPinpoint Lead the Market
For most businesses, AirTags and AirPinpoint Tags offer the best combination of affordability, reliability, and ease of use. While GPS trackers have their place in niche scenarios, the cost and maintenance overhead often outweigh their benefits.
AirPinpoint's enterprise-grade solutions provide businesses with unmatched scalability, security, and integration capabilities—making them the clear choice for modern asset tracking.