The Future of Asset Inventory Management: Zero-Touch Automation in 2025
Traditional inventory management methods cost businesses up to 35% more than automated solutions—while simultaneously delivering 23% lower accuracy rates. As we move deeper into 2025, the evolution from manual to zero-touch automated inventory systems is revolutionizing how businesses track and manage their assets.
This comprehensive guide explores the transformation from barcode scanning to RFID systems, and now to the latest innovation: GPS-based automated check-in/check-out systems that operate with zero human intervention.
Table of Contents
- The Evolution of Asset Inventory Management
- RFID Inventory Tracking: The Current Standard
- The Game-Changer: GPS-Based Automated Asset Management
- Implementing Zero-Touch Inventory Management
- ROI Analysis: The Business Case for Automation
- Case Studies: Organizations Transforming Through Automation
- Future Developments on the Horizon
- FAQs: Automated Inventory Management Systems
The Evolution of Asset Inventory Management
The journey toward automated inventory management has evolved through distinct technological phases, each solving limitations of previous approaches:
Phase 1: Manual Inventory Management (Pre-2000s)
- Paper-based tracking systems
- Physical counts and manual record-keeping
- Error rates of 10-15%
- Labor-intensive processes
Phase 2: Barcode Revolution (2000-2010)
- Introduction of barcode scanning technology
- Semi-automated data entry
- Reduced error rates to 5-8%
- Still required manual scanning of each item
Quote: "Barcode technology cut our inventory processing time in half, but we still needed staff to physically scan each item. The process remained vulnerable to human error and avoidance." — Sarah Chen, Operations Director, TechSupply Inc.
Phase 3: RFID Transformation (2010-2020)
- Implementation of RFID inventory tracking systems
- Passive detection of multiple items simultaneously
- Error rates below 2%
- Reduced but still necessary human intervention
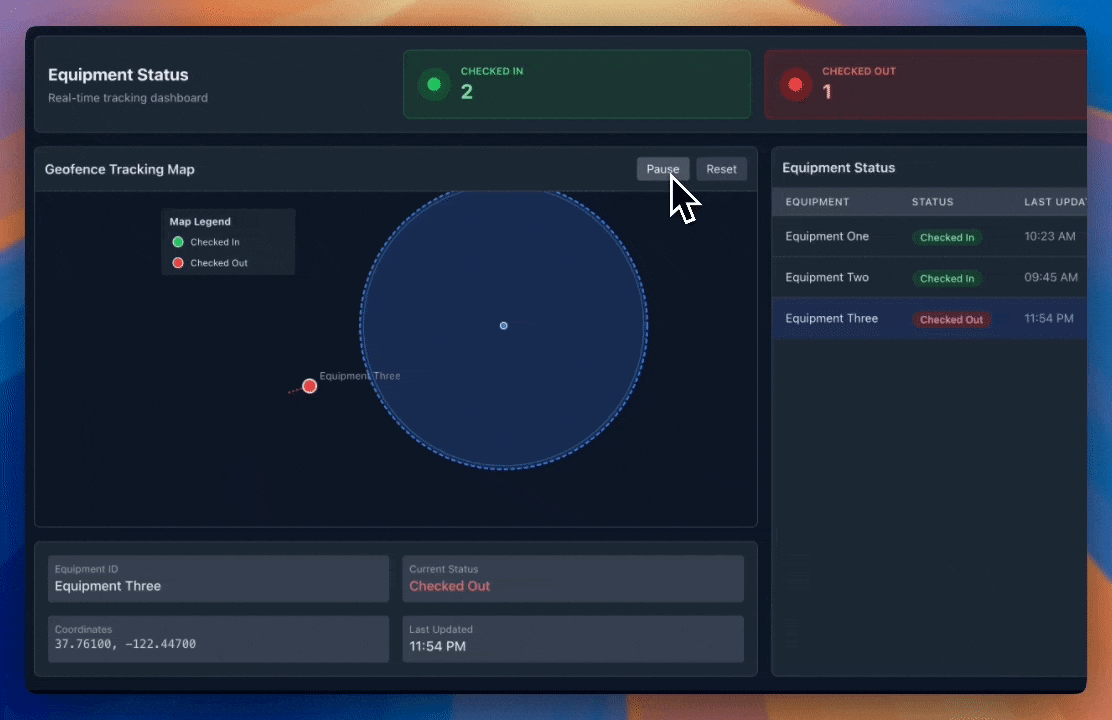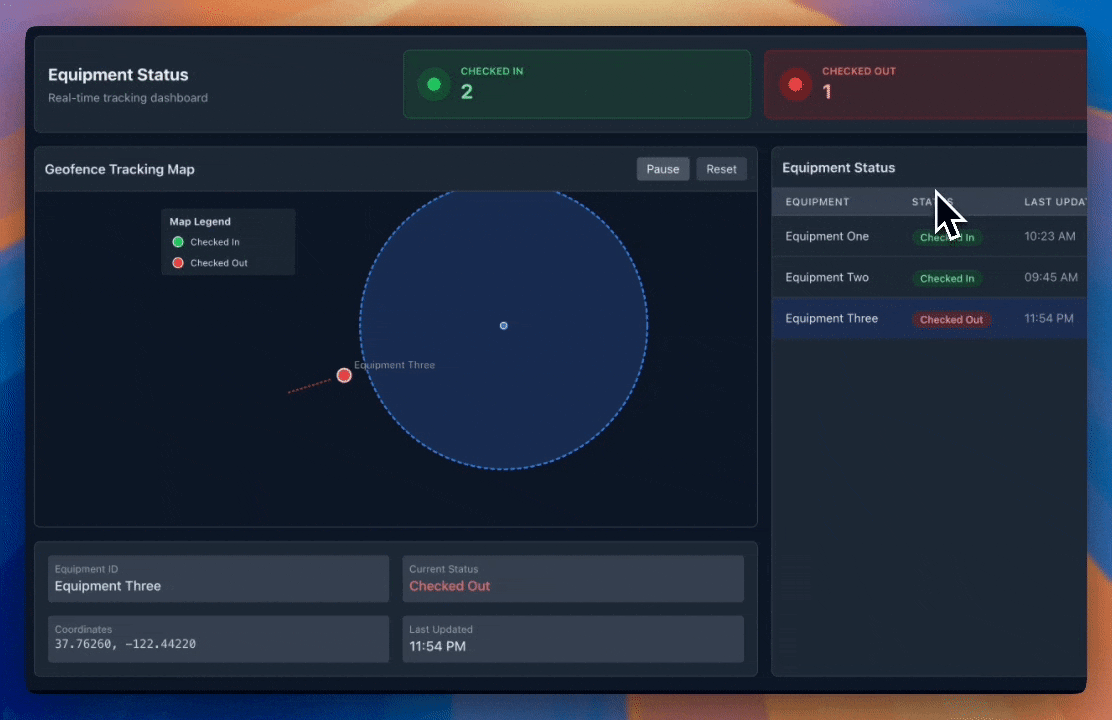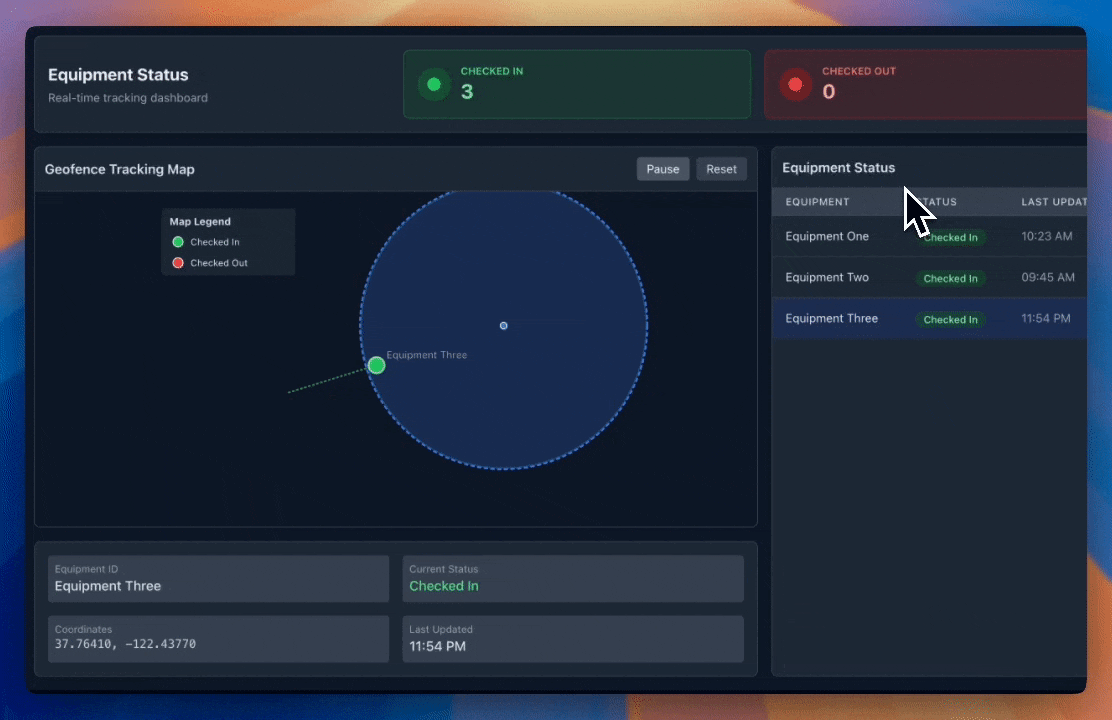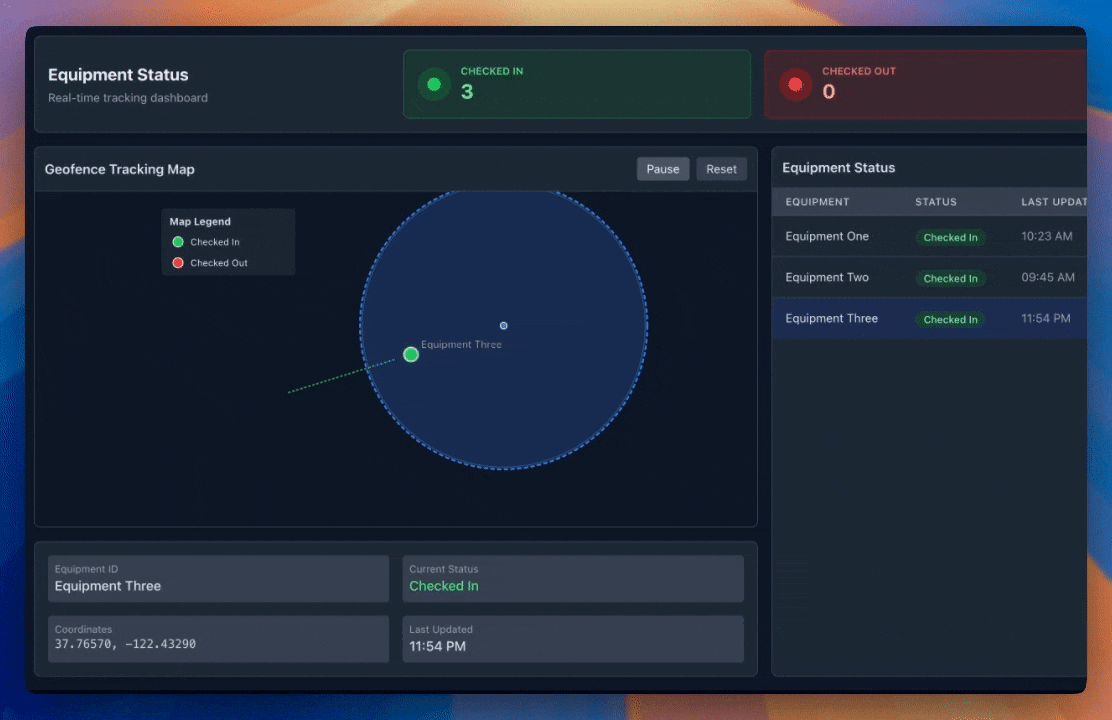
Phase 4: GPS Automation (2024-Present)
- GPS tracking technology with geofencing capabilities
- Real-time location awareness
- Fully automated check-in/check-out
- Zero human intervention required
- Error rates below 0.5%
This evolution represents the industry's progression toward frictionless, accurate, and efficient asset inventory management systems.
RFID Inventory Tracking: The Current Standard
RFID inventory tracking systems have become the backbone of modern inventory management over the past decade, with solid benefits but inherent limitations:
How RFID Inventory Systems Work
RFID technology uses radio waves to identify and track tags attached to objects. A typical RFID inventory management system includes:
- RFID Tags: Attached to inventory items, containing unique identifiers
- RFID Readers: Installed at strategic locations to detect tag movement
- Middleware: Software that processes and interprets tag data
- Inventory Management Software: System that updates inventory records based on tag movement
Advantages of RFID Inventory Systems
| Advantage | Description | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Simultaneous Scanning | Multiple items detected at once | 70-80% reduction in processing time |
| Non-Line-of-Sight Reading | Tags can be read without visual contact | Improved scanning reliability and speed |
| Durability | Tags withstand harsh environments | Lower replacement costs than barcodes |
| Data Capacity | Store more information than barcodes | Enhanced asset data management |
| Real-Time Tracking | Continuous monitoring of tagged items | Improved inventory accuracy |
Limitations of RFID Systems
Despite their advantages, RFID inventory tracking systems have noteworthy constraints:
- Limited Range: Typically 1-30 feet depending on tag type
- Gateway Dependence: Requires fixed reader infrastructure
- Metal/Liquid Interference: Signal disruption from certain materials
- Infrastructure Costs: Significant reader installation expenses
- Partial Automation: Still requires some human intervention
- Indoor Focus: Limited effectiveness in large outdoor areas
These limitations have created demand for the next evolution in asset inventory management: GPS-based automated systems.
The Game-Changer: GPS-Based Automated Asset Management
The latest revolution in asset inventory management integrates GPS tracking technology with geofencing to deliver truly zero-touch automation:
How Automated GPS Asset Management Works
- GPS-Enabled Asset Tags: Small trackers attached to valuable assets
- Geofence Definitions: Virtual boundaries established around storage areas, job sites, or facilities
- Cloud-Based Monitoring: Real-time location awareness and boundary monitoring
- Automated Status Updates: System automatically registers check-in/check-out events when assets cross geofence boundaries
- Notification System: Alerts for unauthorized movements or schedule deviations
The Zero-Touch Revolution
Modern GPS-based inventory systems eliminate the need for any manual scanning or human intervention in the check-in/check-out process:
- Assets are automatically registered as "checked out" when they leave a designated storage area
- Assets are automatically marked as "returned" when they re-enter the storage zone
- Location history is maintained for audit and analysis purposes
- Utilization data is automatically compiled for efficiency analysis
- Maintenance scheduling is triggered by usage metrics, not manual reporting
Quote: "Our previous RFID system required gateway installations and still needed staff to verify movements. With our new GPS-based system, assets automatically check themselves in and out as they move through geofence boundaries. We've eliminated human error while gaining unprecedented visibility." — Marcus Johnson, Logistics Director, BuildRight Construction
Comparative Analysis: Barcode vs. RFID vs. GPS Automation
| Feature | Barcode | RFID | AirPinpoint Automation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee Intervention | High (manual scanning) | Medium (gateway monitoring) | None (fully automated) |
| Real-Time Location | No | Limited (at chokepoints) | Continuous (anywhere) |
| Range | Line of sight only | 1-30 feet | Global coverage |
| Installation Complexity | Low | High (fixed infrastructure) | Low (no fixed infrastructure) |
| Error Rate | 5-8% | 1-2% | <0.5% |
| Automation Level | Low | Medium | High |
| Outdoor Effectiveness | Poor | Limited | Excellent |
| Cost Per Asset | $0.05-0.15 | $0.10-5.00 | $4-7 |
| Labor Cost Per Asset Per Month | $15-25 | $8-12 | $0 |
| Infrastructure Cost | Low | High | Low |
Implementing Zero-Touch Inventory Management
Transitioning to an automated inventory management system requires strategic planning and implementation:
1. Assess Asset Value and Mobility
Determine which assets justify GPS tracking based on:
- Financial value
- Operational importance
- Mobility requirements
- Loss/theft risk
- Utilization monitoring needs
High-value assets with frequent movement are ideal candidates for GPS-based automation.
2. Select Appropriate Tracking Technology
Choose tracking technology based on specific requirements:
- Active GPS Trackers: For high-value assets requiring real-time visibility
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Tags: For indoor tracking within defined spaces
- Hybrid RFID/GPS Solutions: For comprehensive facility and field coverage
- Cellular-Enabled Trackers: For assets moving between remote locations
3. Define Geofence Boundaries
Establish virtual boundaries around:
- Warehouses and storage facilities
- Job sites and work areas
- Client delivery locations
- Restricted zones
- Maintenance areas
4. Integrate with Existing Systems
Connect automated inventory management with:
- ERP and accounting systems
- Maintenance management software
- Project management tools
- Purchasing and procurement systems
- Security systems
5. Establish Monitoring Protocols
Define automated alert conditions for:
- Unauthorized movement
- Schedule deviations
- Excessive idle time
- Maintenance needs based on usage
- Battery replacement requirements
ROI Analysis: The Business Case for Automation
The investment in GPS-based automated inventory management typically delivers ROI within 4-8 months through:
Direct Cost Savings
- Labor Reduction: 85-95% decrease in time spent on inventory tasks
- Loss Prevention: 92% reduction in lost or misplaced assets
- Theft Deterrence: 78% decrease in theft incidents
- Utilization Improvement: 25-35% better asset utilization rates
- Maintenance Optimization: 22% reduction in maintenance costs through usage-based scheduling
Indirect Benefits
- Project Efficiency: Eliminated delays from missing equipment
- Decision Support: Data-driven asset purchasing decisions
- Client Satisfaction: Improved service delivery reliability
- Audit Compliance: Automated documentation of asset movements
- Insurance Advantages: Premium reductions for tracked assets
Sample ROI Calculation for Mid-Sized Business (100 Tracked Assets)
| Category | Annual Cost Before | Annual Cost After | Annual Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Staff Time (inventory tasks) | $78,000 | $7,800 | $70,200 |
| Asset Loss/Theft | $45,000 | $5,400 | $39,600 |
| Unnecessary Rentals/Purchases | $38,000 | $19,000 | $19,000 |
| Maintenance Optimization | $65,000 | $50,700 | $14,300 |
| Administrative Overhead | $32,000 | $8,000 | $24,000 |
| TOTAL ANNUAL SAVINGS | $167,100 |
With typical implementation costs of $40,000-$60,000 for a 100-asset system, the ROI is compelling and rapid.
Case Studies: Organizations Transforming Through Automation
City of Portland Public Works Department
Challenge: Managing 450+ pieces of equipment across multiple sites with frequent transfers
Solution: Implemented GPS-based automated inventory system with geofencing
Results:
- Equipment theft reduced by 94%
- $315,000 in recovered stolen equipment in first year
- Utilization rates improved by 28%
- Eliminated 1,850 staff hours previously dedicated to equipment tracking
- Annual savings: $425,000
National Hospital Network
Challenge: Tracking thousands of mobile medical assets across 12 facilities
Solution: Hybrid RFID/GPS system with automated check-in/check-out
Results:
- Equipment hoarding reduced by 73%
- Purchasing requirements decreased by 26%
- Staff time searching for equipment reduced by 91%
- Patient care delays related to equipment availability eliminated
- Annual savings: $2.1 million
Future Developments on the Horizon
The next wave of innovation in automated inventory management includes:
1. Miniaturization and Extended Battery Life
- Smaller GPS trackers with multi-year battery life
- Micro-tracking technology for smaller assets
- Energy harvesting to create self-powered trackers
2. Enhanced AI Integration
- Predictive analytics for maintenance needs
- Automated reordering systems
- Anomaly detection for unusual usage patterns
- Behavior analysis to spot potential theft or misuse
3. Edge Computing Capabilities
- Distributed processing for faster responses
- Reduced cellular data consumption
- Enhanced offline functionality
- Local decision-making without cloud dependency
4. Extended Monitoring Capabilities
- Environmental monitoring (temperature, humidity, etc.)
- Usage pattern recognition
- Operational diagnostics
- Safety compliance monitoring
FAQs: Automated Inventory Management Systems
Q: How does zero-touch automated inventory differ from traditional RFID systems?
A: Traditional RFID systems require fixed infrastructure (readers at doorways/gates) and only track assets when they pass through these checkpoints. Zero-touch automated GPS systems offer continuous real-time tracking anywhere, automatically updating status as assets move through geofenced boundaries without requiring any fixed infrastructure or manual intervention.
Q: What types of assets are best suited for GPS-based automated inventory?
A: High-value mobile assets justify GPS tracking investment, including:
- Construction equipment and machinery
- Fleet vehicles and specialized transport
- Medical equipment and devices
- IT assets and mobile technology
- Field service equipment and tools
- Rental equipment
- Shared organizational resources
Q: How do automated systems handle indoor locations where GPS signals are weak?
A: Modern solutions employ hybrid approaches:
- Bluetooth beacons for precise indoor positioning
- Wi-Fi triangulation as a GPS supplement
- RFID for specific chokepoints
- Cellular-assisted GPS location
- Signal processing algorithms to enhance weak GPS signals
Q: What security measures protect automated inventory systems?
A: Enterprise-grade systems include:
- End-to-end data encryption
- Multi-factor authentication
- Role-based access controls
- Event logging and audit trails
- Tamper-evident hardware
- Anti-jamming technology
- Backup communication methods
Q: How do you measure ROI for automated inventory management?
A: Key metrics to track include:
- Labor hour reduction in inventory processes
- Asset loss/theft reduction
- Asset utilization improvement
- Maintenance cost reduction
- Administrative overhead reduction
- Unplanned downtime reduction
- Opportunity cost savings from improved availability
- Reduction in unnecessary rentals or purchases
Transform Your Asset Management Today
The progression from barcodes to RFID to GPS-powered zero-touch automation represents the most significant evolution in inventory management history. Organizations embracing this technology are experiencing unprecedented efficiency, accuracy, and visibility.
The true power of automated inventory management lies in its ability to remove human error and intervention from the equation while delivering richer data and insights than ever before.
Contact our inventory automation specialists for a demonstration of how zero-touch asset management can transform your operations.
This guide was last updated on May 10, 2025, with the latest industry data and technology information.
